Environment Class 12
REVISION OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS (5:07 PM):
- The biospheres contain flora and fauna in their most pure state.
- The analysis of these areas would help in better understanding human impacts in other areas.
Man And Biosphere (MAB)Program:
- UNESCO launched the Man & Biosphere Program (MAB) in 1971.
- The program aimed at establishing a scientific basis for improving the relations between people and their environment.
- This scientific basis is based on the principles:
- I. Natural Sciences.
- II. Social Sciences
- III. Economics
- IV. Education.
- The scientific basis is created from a clear understanding of how ecosystems function in their most natural state and how ecological processes work in these regions.
Benefits of the analysis:
- This knowledge is a reference to understanding changes due to man-related and natural-related causes in comparable ecosystems.
- This provides an understanding of how man's actions have changed the natural ecosystems.
- To examine the nature of interactions between man, nature and also understand the pattern of resource use and exploitation.
- In biosphere reserves, the resource-use pattern has not led to any significant adverse impact on natural resources and ecosystems.
- Therefore, this pattern of human activity could be integrated with models of social & economic development.
- This will result in development without adversely impacting the ecosystem.
- Hence, sustainable development strategies can be designed based on such patterns of human activity to be implemented at different levels- local to international.
- The MAB accepts that modern industrial development, urban development, and energy have caused serious damage to natural resources and ecosystems.
- MAB, therefore, seeks to understand what kind of impact these activities had on ecosystems.
- Based on this knowledge, alternative models of industrial & urban development and energy production can be designed.
- This can lead to the formation of sustainable development models.
- When researchers study biosphere reserves worldwide in different geographic and cultural settings, a clear understanding of how ecological processes and ecosystems work in different conditions is generated.
- This improves basic knowledge and also helps in developing the right types of conservation strategies.
BIOSPHERE RESERVES (5:40 PM):
- They have been created as protected areas by the International Coordinating Council (ICC) of the MAB program in 1971.
- They represent natural biomes, natural resources, ecological processes & ecosystems in their most natural state.
- Protecting them as biosphere reserves will preserve the last few regions on the earth's surface where nature is present in its most natural state.
- Being in a pristine state, they are a very good source of baseline information for knowledge, research, and practical applications like the right strategy.
- They have unique communities of biodiversity and also unusual features of great scientific value.
- They may have unique landscapes or species.
- They may have degraded ecosystems capable of being restored to their natural state.
- Since they include some communities of man exploiting the resources without causing harm to the ecosystem, they provide examples of sustainable use of resources.
- This can be used to develop sustainable development strategies, which can be included in socio-economic development models.
- As these regions allow natural and evolutionary processes to continue without interference from man, they are needed for sustainable evolution on Earth.
- Since communities have been interacting with ecosystems in these regions, it will provide ideas for developing conservation strategies involving local participation.
- They are protected under Category V of the IUCN classification.
-
ZONES IN A BIOSPHERE RESERVE (6:10 PM):

- Core:
- This can be understood as the central region of the biosphere reserve.
- They have natural resources in an almost pure state.
- This will have the highest degree of biodiversity, endemism, and protection.
- No human activities are allowed in this area except research and training.
- Conservation projects are usually designed based on the core zone.
- The core has a well-defined boundary.
Buffer zone:
- This zone is situated between the core and the outermost transition zone.
- This is rich in biodiversity, but it has been altered to some extent by man.
- Limited human activities(tourism, recreation grazing, etc), without adverse impact on the core, are allowed.
- Ecosystem restoration and demonstration projects are taken up here.
- The buffer zone also has a well-defined boundary.
Transitional zone:
- This is the outermost zone of a biosphere.
- The region has no well-defined boundaries.
- All land use patterns and human activities are allowed, but based on improved skills to minimize the effects on the biosphere reserve.
- It is important to allow some human activities here because otherwise, people might be forced to enter buffer and core zones.
WORLD NETWORK OF BIOSPHERE RESERVES (6:35 PM):
- The ICC of MAB created the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in 1976 with the objectives of promoting economic, social, and environmental sustainability.
- They include the most important regions of biodiversity in the world.
The aims are:
- Develop and maintain regions of ecological and cultural diversity.
- Strengthen the ecosystem services for human well-being.
- Develop and integrate knowledge that is created from the study of these networked biosphere reserves.
- Capacity building by creating a pool of conservationists and researchers for management.
-
Capacity Building:
- This refers to training the concerned communities in the skills and behavioral patterns required to fulfill any goal.
- For example, capacity building for fishermen would include providing them with information, capital, and equipment which would help them in catching more fish.
- Information regarding fish breeding grounds, seasons, techniques to get more harvest, better nets, cold storage for the fish, etc. would be included.
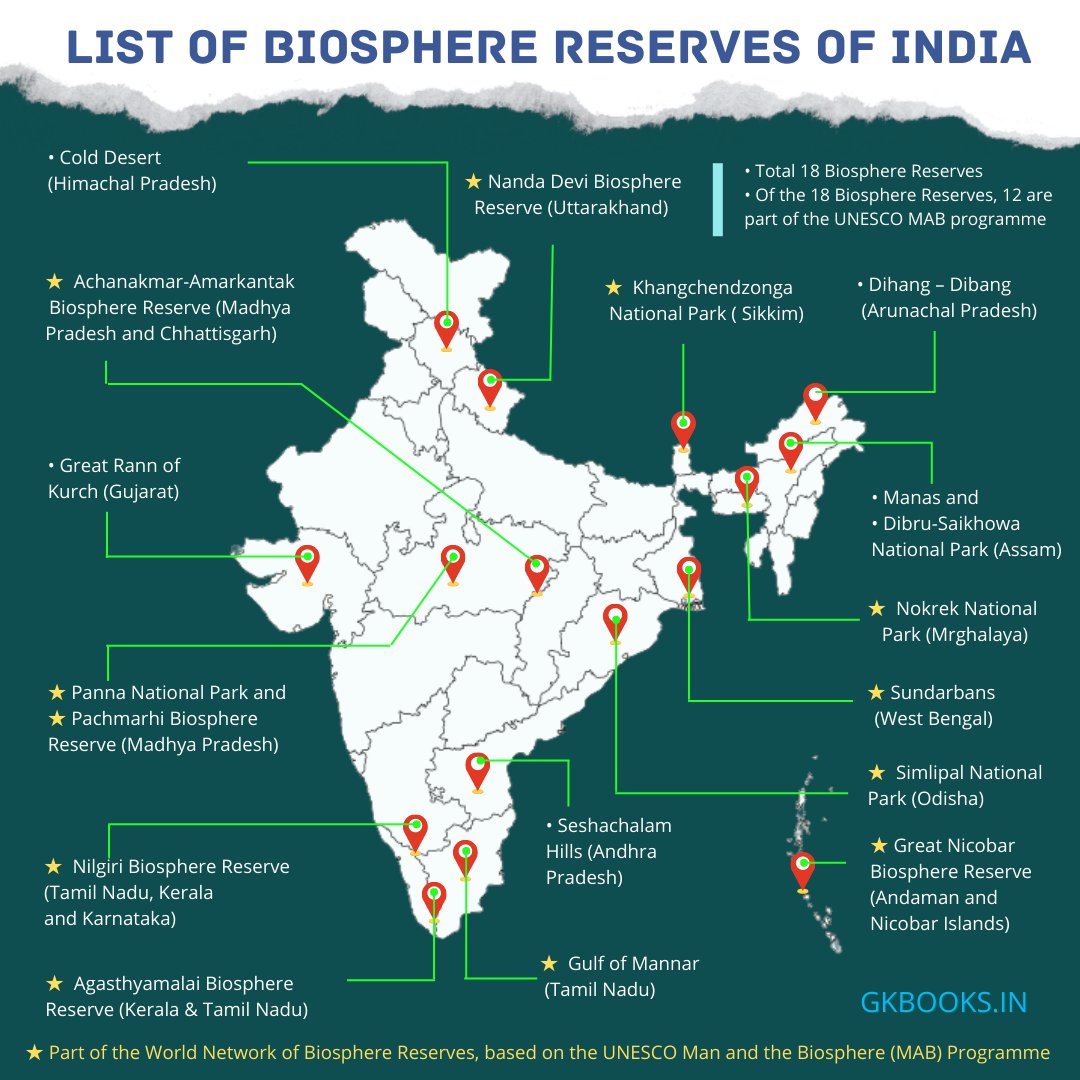
- Nilgiri, Gulf of Mannar, Sundarbans, Panna, etc. are some biosphere reserves that are part of the network.
CONVENTION ON BIODIVERSITY (CBD) (7:15 PM):
- It was finalized at Rio Earth Summit in 1992.
- The first objective was to conserve biodiversity.
- The second objective is to use biological resources in a sustainable manner.
- The third objective is a fair and equitable share of benefits arising from biodiversity.
- Traditional knowledge and practices which have been preserved and used for centuries must be recognized.
- If any company wishes to utilize traditional knowledge commercially, that must be done only after the informed consent of the communities concerned.
- India passed the Biological Diversity Act, of 2002 to comply with the convention.
- Under the act, Biodiversity Management Committees must collect traditional knowledge at local levels for storage and legal registration.
KEY PROVISIONS OF CBD (7:35 PM):
- Countries have sovereign rights over the biological resources within their territory and therefore can control access to it.
- On-site conservation should be the key conservation strategy to maintain biodiversity in its natural form.
- Developed countries have an obligation to transfer funds to developing countries so that they are able to meet the cost of conservation.
- Developed countries are also obliged to transfer technologies to developing countries for effective conservation & sustainable use of biodiversity.
- Users of biological resources should compensate communities who have contributed to traditional knowledge on the use of biodiversity for certain purposes.
Cartagena Protocol on Biodiversity 2000:
- It is a part of the CBD.
- Biosafety refers to the need to protect human and environmental health from the possible adverse effects of the products of biotechnology.
- The protocol declares that developed countries should transfer technologies for biosafety to developing countries.
- It calls upon all countries to develop procedures to improve safety while using products of biotech.
- It is for safe handling, packaging, transportation, and use of Living Modified Organisms( LMOs) resulting from modern biotechnology.
- The protocol deals with the safe and sustainable usage of transgenic crops/animals.
- Transgenic crops/animals are those which have their DNA modified using genetic engineering.
- This is done to include certain desirable characteristics in the species.
- Bt Cotton is the only transgenic crop sown in India; it shows higher resistance to pests than normal cotton.
- The protocol also lays down the standards to be compulsorily followed during transboundary movements of LMOs.
- There must be informed consent from both the importers and exporters of LMOs.
- Both parties must be clear about the possible uses and dangers associated with the LMOs.
The topics for the next class are Nagoya Protocol, Aichi Targets, Indian steps taken, Ecosensitive Zones, etc.